Salary & Bonuses
The estimated average salary increase of all respondents was 4.75%, with public companies awarding the highest salary increases (4.96%). The two industries with the highest reported salary increases were advertising (8%) and metals (7.5%).
For the second year in a row, the base salaries of public and private company CFOs were proportionate to the annual revenues of their employers. However, median base salaries for public company CFOs with less than $25 million or over $5 billion in annual revenues are generally consistent or slightly higher from the prior year. No public company CFOs from companies with annual revenues of less than $25 million earned more than $400,000 per year.
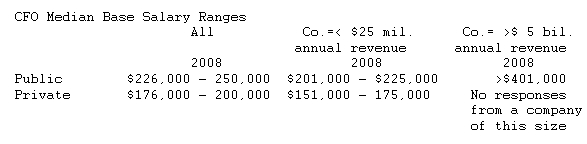
With regard to bonuses, annual bonuses of private company CFOs were lower than those of public company CFOs. Most bonus percentages for public company CFOs fell within the range of 21-70%, while those of private company CFOs fell within the range of 11-60%. The study also showed that many public companies with annual revenues of $99 million or less received discretionary bonuses.
Beyond the Paycheck
For the second year in a row, the trend indicates more specialized technical and compliance-type responsibilities at public companies, which include legal, purchasing, operations, investor relations, planning, M&A, and Sarbanes-Oxley compliance. Additionally, private company respondents reported more responsibility in the areas of treasury, tax, human resources, administration and risk management/insurance than their public company counterparts.
"As we all know, executive compensation is more than just salary, and this study continues to examine the structure of pay packages in their entirety," said Cheryl de Mesa Graziano, Vice President, Research and Operations for FERF. "The results of this year's study showed decreases in other compensation benefits, such as long-term and retirement incentives, and we feel this helps to illustrate a complete and clearer picture of the overall impact that the broader economy has on financial executives."
Key statistics from areas additional to salary and bonus include:
Retirement
- The number of respondents eligible for their company's defined benefit
plan saw an overall increase from 2007
- The overall number of supplemental retirement plans decreased from 2007.
- A significant majority of respondents are not entitled to receive additional monthly retirement benefits
Long-term incentives
- 20.3 percent were eligible to receive cash-based long-term incentive compensation (of those 43.6 percent were from public companies and 50.4 percent from private companies), a decrease from last year
- Stock-based awards decreased from 2007, as many respondents noted that their target award is based on a fixed number of shares or units
Perks
- Most popular perk continues to be company car or car allowance (29 percent of CFOs receive)
- Least popular perk continues to be housing or other living expenses (2 percent of CFOs receive)
Performance measures
- Most common performance measures used to determine annual compensation were company and individual goals and objectives
- Company Goals/Objectives (Nearly 79 percent of public company respondents)
- Individual Goals/Objectives (75 percent of public company respondents)
The report includes detailed tables of the base salary and annual bonus for each major title, and is broken down further by company's annual revenue and public or private status. To purchase the survey report for $129, visit the FERF bookstore online at www.ferf.org/bookstore.





